
Doctors recommend every newborn baby to undergo newborn screening tests, within 24-72 hours after delivery. Newborn screening is a process for diagnosing certain harmful or potentially fatal disorders which are otherwise not visible during childbirth. It is a process by which infants are put on screening for a number of congenital metabolic disorders, which are treatable, but not detectable clinically. As such, doctors conduct a simple blood test to determine whether a newborn is born with certain conditions that can eventually cause health problems. Although these conditions are generally rare and most babies are given a clean health chit, but it is always better to diagnose early and begin with the treatment in order to help the baby nurture into a strong and fit individual. An early diagnosis of a congenital disorder can assist you in following your doctor’s treatment and saving your baby from lifelong health and developmental issues. A few drops of blood are pricked from the baby’s heel in between 24-72 hours after birth and put on a special absorbent card to let the blood dry. The sample is then sent to the laboratory meant specifically for testing newborn screening samples. In case the reports turn positive and the baby is diagnosed with any disorder, further tests are performed for additional evaluation and determination of the kind of treatment for the said condition. Know the different benefits of newborn screening and the various disorders that can be diagnosed with this test. Read on.

Image Credit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vxshWngJ114
Newborn Screening
Newborn screening is carried out for certain reasons:
-
Firstly, newborn screening detects whether a newborn is capable of undergoing this test for genetic conditions, which can eventually transform into mental retardation, serious health complications, and death, if left untreated and undetected.
-
Newborn screening helps in creating awareness amongst all medical practitioners about this test and identifying their respective roles in offering a newborn with the opportunity to undergo this test.
-
Finally, newborn screening is carried out to help parents recognize their responsibility towards contributing to the right health and full development of their baby. By detecting the disorders at an early stage, parents can protect their baby from preventable causes by resuming to early treatment.
Researches state that newborn screening is highly beneficial for testing blood samples of a baby for more than 100 disorders, including over 50 congenital conditions. Perhaps, only one out of 5,000 babies turn positive for one of the metabolic tests, excluding congenital infections. Some of the most commonly tested disorders using newborn screening are listed below.
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder that is characterized by the lack of a special enzyme that is essential for metabolizing a protein compound called phenylalanine. Due to the absence of phenylalanine, phenylketones, or toxic substances that destroy brain cells get accumulated; thus, resulting in mental retardation. The brain cells, once damaged, cannot be repaired, while mental retardation is deemed as an irreversible condition.
Galactosemia
When galactose is not metabolized, it is likely to get accumulated in the bloodstream. This, in turn, results in liver enlargement, renal problems, cataracts, and brain retardation. If left untreated, galactosemia can further trigger multiple organ damage, and even death.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a condition where regulating hormones produced by adrenal glands are affected extensively. As a result, the development of secondary sex characteristics of the infant are highly altered, which can even be fatal, due to the loss of salt in the kidneys.
Biotinidase Deficiency
If your baby is diagnosed with biotinidase deficiency, his body would be unable to produce the enzyme crucial for metabolizing biotin, a B-complex vitamin. This vitamin is essential for maintaining the health of the nervous system and immune system, the absence of which can result in seizures, hearing loss, poor muscle control, mental retardation, and death.
Sickle-cell Anemia
The reshaping of red blood cells into that of a sickle is largely responsible for altering their oxygen-carrying capacity. Plus, sickle-cell anemia inclines an infant towards a variety of infections, like pneumonia and meningitis.
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
MSUD is a disorder wherein the baby lacks the enzymes in the body necessary for breaking down three essential amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. The presence of these three amino acids produces urine that smells like burnt sugar or maple syrup, thereby leaving behind some toxic by-products. As a result, the baby is likely to suffer from vomiting, dehydration, lethargy, and poor muscle tone.
Other Disorders
Apart from the above stated disorders, newborn screening also assists in diagnosing several other health problems, such as congenital hypothyroidism; hearing impairment; cystic fibrosis; organic acid metabolism disorders like propionic academia, beta-ketothiolase deficiency, glutaric academia, methylmalonic academia, isovaleric academia, and multiple carboxylase deficiency; fatty acid oxidation disorders like carnitine uptake defect and trifunctional protein deficiency; and amino acid metabolism disorders like citrullinemia, argininosuccinic academia, and tyrosinemia type I.
An early detection of any disorder or health condition can help start the treatment, thereby reducing expensive risks at a later stage. Create a significant difference between lifelong impairment and healthy development by opting for newborn screening.
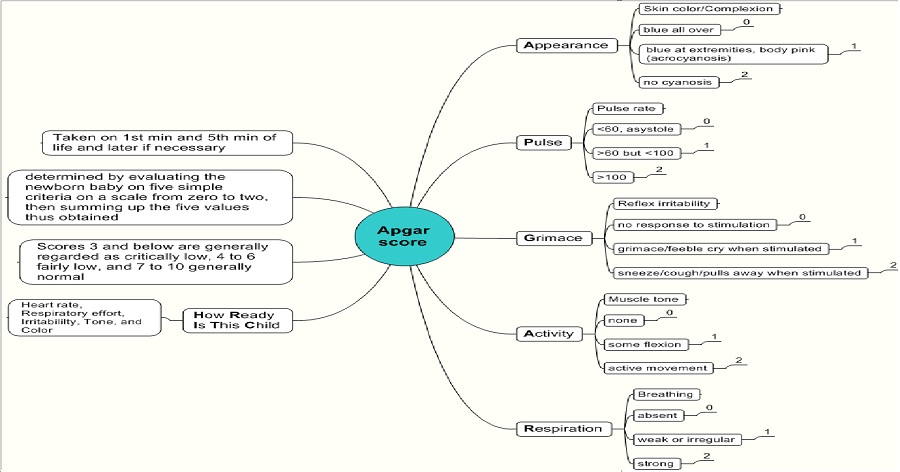 APGAR Score
APGAR Score Excessively Crying Baby: Reasons & Remedies to Comfort Your Infant
Excessively Crying Baby: Reasons & Remedies to Comfort Your Infant Baby Pacifiers Guide: Advantages, Disadvantages And How To Wean The Baby From A Pacifier
Baby Pacifiers Guide: Advantages, Disadvantages And How To Wean The Baby From A Pacifier Shaken Baby Syndrome
Shaken Baby Syndrome Step-By-Step Guide To Burp Your Baby: How and When?
Step-By-Step Guide To Burp Your Baby: How and When? Types of Diaper Rash: Tips & Home Remedies To Treat Nappy Rash Naturally
Types of Diaper Rash: Tips & Home Remedies To Treat Nappy Rash Naturally A Step-By-Step Guide on Infant Sleep Training: Baby Sleep Methods, Sleep Schedule & Sleep Position
A Step-By-Step Guide on Infant Sleep Training: Baby Sleep Methods, Sleep Schedule & Sleep Position Baby Safety Products
Baby Safety Products